
E Ink is the inventor of several types of electrophoretic ink, often called electronic ink. When laminated to a plastic film, and then adhered to electronics, it creates an Electronic Paper Display (EPD). Although futuristic-sounding, electronic ink is actually a straightforward fusion of chemistry, physics and electronics. It's so much like paper, it utilizes the same pigments used in the printing industry today.
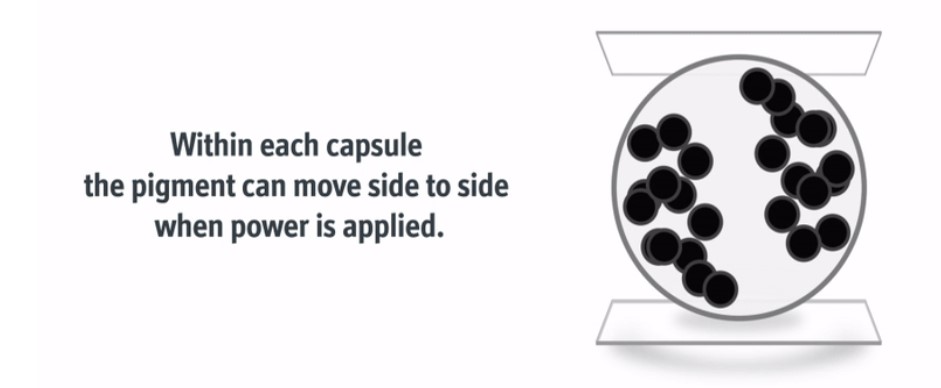
E Ink JustTint™ is a variable transmissive film, which, when adhered to glass or plastic, allows for control of the light through the surface. JustTint utilizes a one-pigment system, but drives the ink in new ways versus other ink systems. In JustTint, the black pigments move to the side when a charge is applied to allow a transparent area of the capsule.
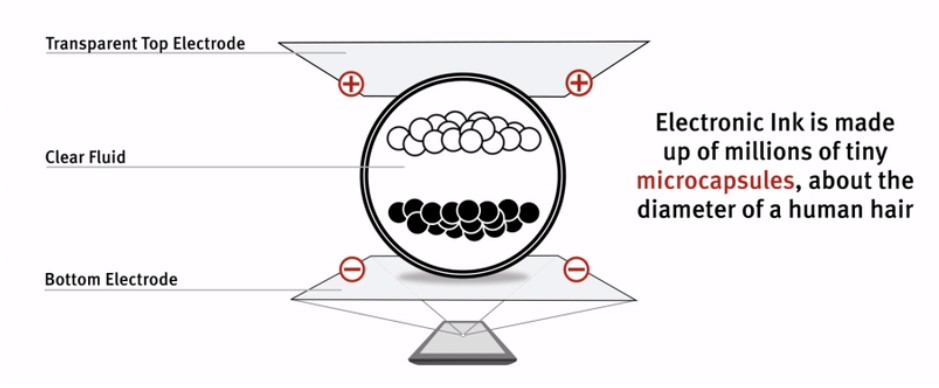
E Ink’s two pigment electronic ink system is made up of millions of tiny microcapsules, each about the diameter of a human hair. Each microcapsule contains negatively charged white particles and positively charged black particles suspended in a clear fluid. When a positive or negative electric field is applied, corresponding particles move to the top of the microcapsule where they become visible to the viewer. This makes the surface appear white or black at that spot.E Ink JustWrite™, – this new film delivers a natural writing experience without the use of a TFT backplane or complex electronics. JustWrite utilizes a two-pigment electronic ink system, but drives the ink utilizing a different method from our standard inks. In JustWrite, a magnetic pen is the “driver” to move the ink; to reset the display back, a small electrical charge is applied. JustWrite retains the same image stability of all of our ink platforms and power is only utilized to reset the image.
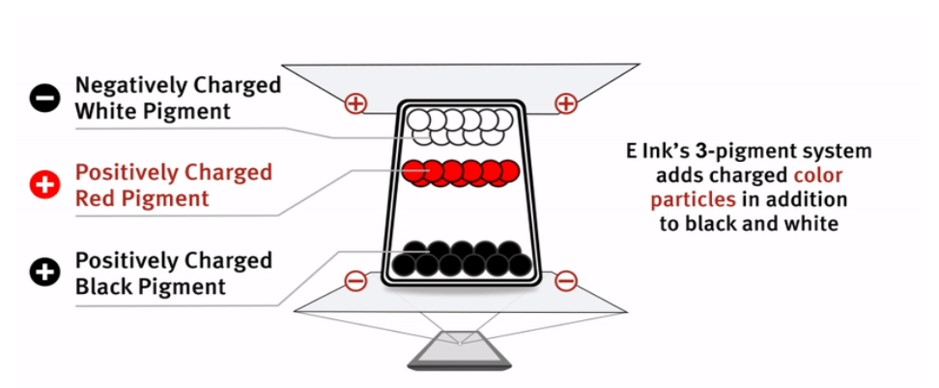
E Ink’s Spectra product line utilizes a 3-pigment ink system in a microcup structure. This ink was engineered specifically for Electronic Shelf Labels (ESL) and is offered in black, white and red. This ink system works similarly to the dual pigment system, in that a charge is applied to the pigments, and to a top and bottom electrode to facilitate movement. However, instead of the use of microcapsules, this system utilizes Microcups®, which are filled with the liquid and sealed.
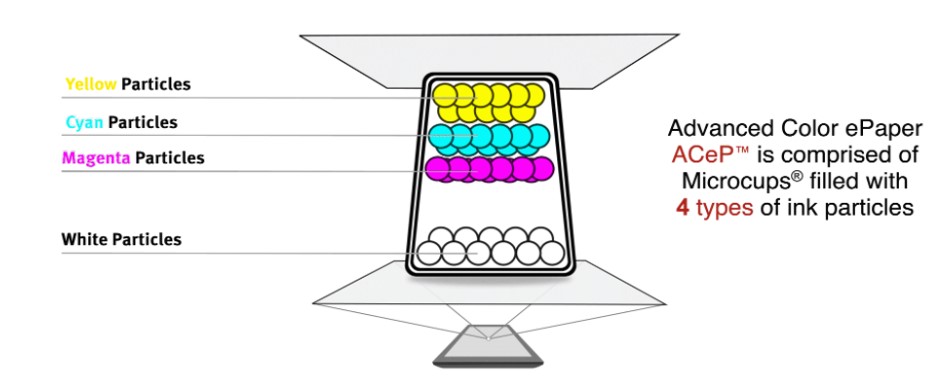
In 2016 E Ink showcased a multi-pigment ink system, Advanced Color ePaper (E Ink ACeP™). ACeP™ achieves a full color gamut, including all eight primary colors, using only colored pigments. The ink can be incorporated into either microcapsule or microcup structures. Color is achieved by having all the colored pigments in every pixel, removing the need for a color filter array. ACeP™ maintains the ultra-low-power and paper-like readability under all lighting conditions of regular E Ink ePaper.
The transmission of wireless energy was an idea born over 100 years ago by famed inventor Nikola Tesla. The global Wireless Charging market is expected to witness a significant growth during the forecast period registering a CAGR of 40.97% and 37.34% in terms of volume and value respectively. Innovations and ongoing research in the consumer electronic devices such as smartphones and IOT devices have been fuelling the growth for wireless charging market. Most wireless power and charging platforms utilize time-varying electric, magnetic, or electromagnetic fields, sound or light to transmit power, and can be broken down into two categories:
Wireless charging or power transfer takes place when energy is transferred as electromagnetic waves from a transmitter to a receiver. On the basis of technology, the Wireless Charging market includes Inductive, Resonant and Radio Frequency (RF) technology-based wireless chargers, among others. Inductive wireless charging technology transfers power using an electromagnetic field from the inductive coupling. The power is transferred from a transmitter using an induction coil to create alternating electromagnetic current, to a receiver coil, thereby creating an electromagnetic field.
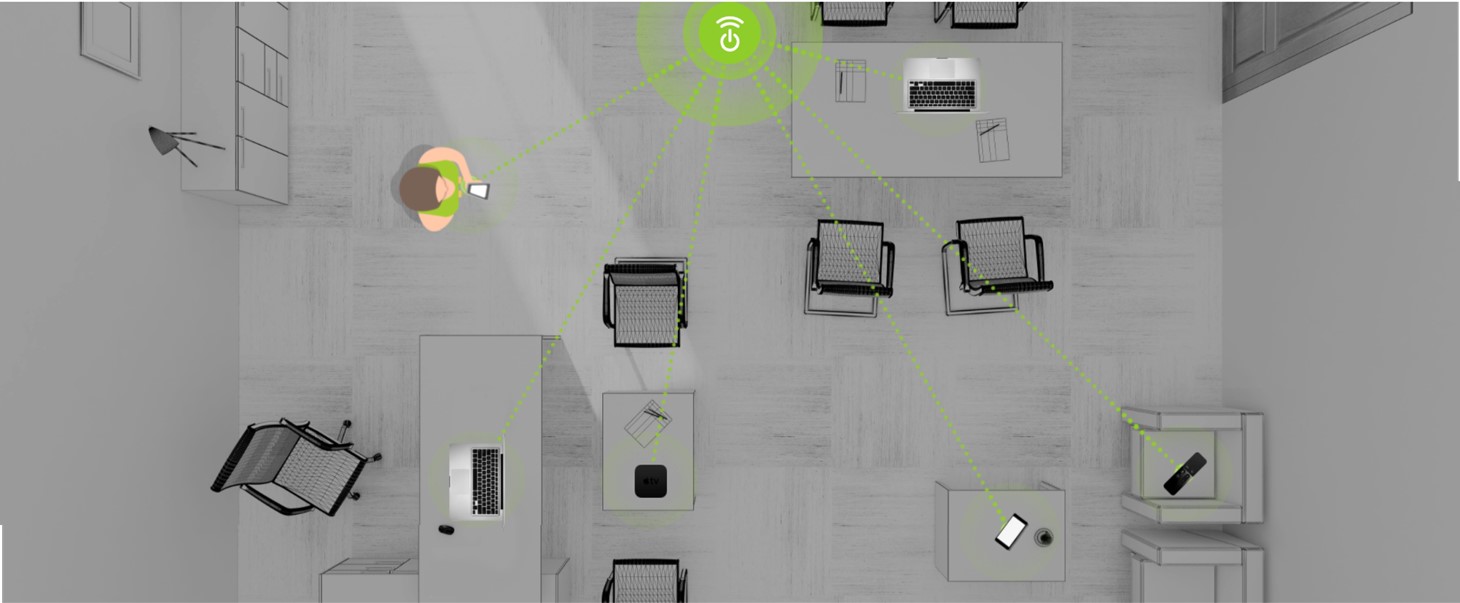
Wireless power solutions could both eliminate batteries and enable completely untethered devices that need no wires or charging surfaces. Long Range Wireless power that could remotely charge enabled devices, would be a game changer for many industries and products. Powercast wireless charging technology – which transmits a radio frequency (RF) whose energy can be “harvested” to power devices embedded with a small receiver.
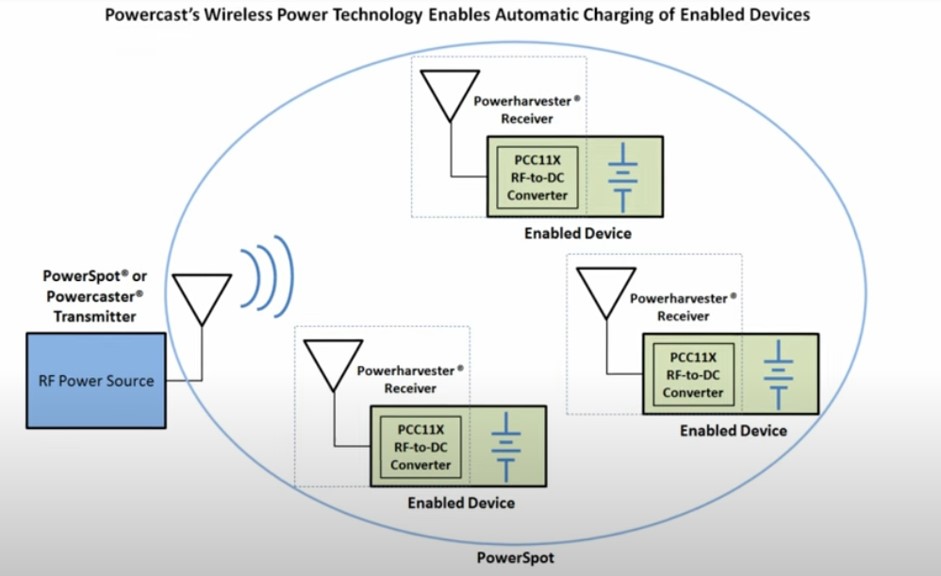
Where enabled devices automatically charge when within range of a transmitter, Powercast’s contactless charging technology provides over-the-air power at a distance to multiple devices – no wires, charging mats or direct line of sight needed. A transmitter sends RF energy to Powercast’s Powerharvester® receiver embedded in a device, which converts it to direct current (DC) to directly power that device or recharge its batteries. Operating across a wide RF power (as low as -17 dBm) and frequency (10MHz to 6GHz) range, the Powerharvester receivers are designed to convert RF to DC with up to 80 percent efficiency.
• Power devices at any distance
• Power multiple devices simultaneously
• Power devices while in motion
• Power devices without line of sight
• Control which devices receive power and when

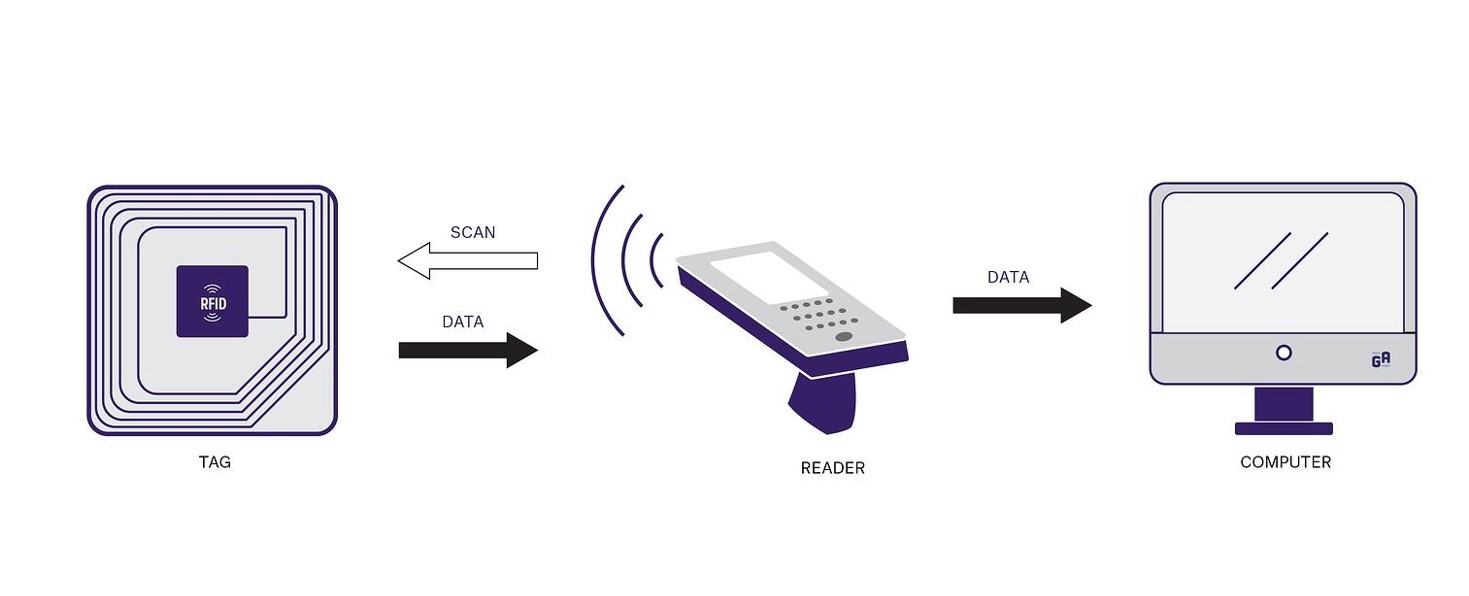
The concept of RFID is not new. However, the technology has evolved over several decades and continues to develop. Rather than a singular technology, RFID is a family of several complimentary radio frequency data capture technologies, each with its own characteristics and strengths. A deep understanding of these technologies is necessary in order to select the most appropriate for a specific application. A list of the common RFID technologies is provided below. Contact Electro-Com for specific recommendations.
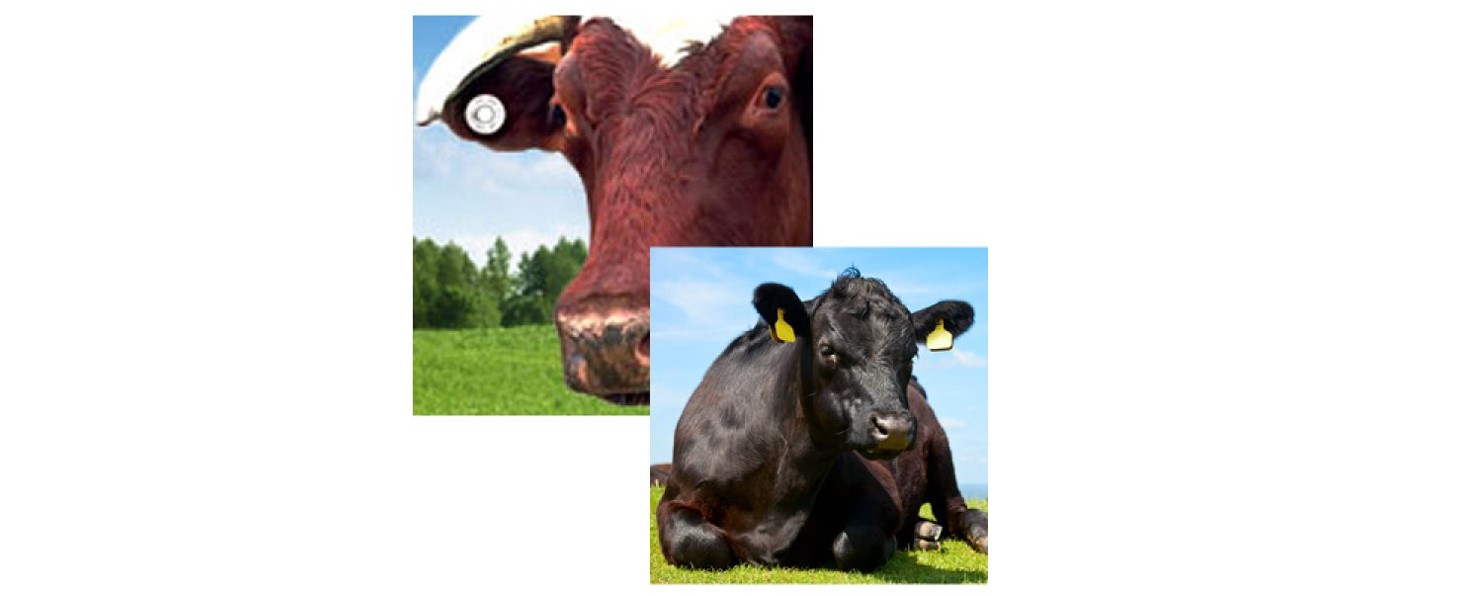
LF RFID technology by Texas Instruments (TIRIS). This class leading half-duplex technology operates on a frequency of 134.2kHz. A major technical break-through when it was introduced in the 1990s, it has proven to be one of the most dependable products on the market and it’s performance is still unmatched. As the basis of the international animal identification standards ISO11784/11785 and automotive security systems, countless millions of tags have been deployed.

HF RFID operates at a frequency of 13.56MHz. HF RFID technologies have been incorporated in International Standards; ISO15693 and ISO14443-A/B and include well known products such as Texas Instruments Tag-it, NXP icode, Mifare etc.With fast data transfer rates, robust performance in most environments, high data storage and low tag costs, HF RFID is widely deployed in many applications including security / access control, passports, ticketing, library automation and asset management.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF) technology is the fastest growing passive RFID technology group. Our extensive range of tags and readers conform to EPCGlobal Class1 Gen2 standards, also referred to as ISO18000-6C or “RAIN” technology. UHF RFID operates between 860MHz to 960MHz (Regulations vary from region to region). All of our UHF products conform to the Australian spectrum requirements. Don’t get caught out importing non-compliant products from Asia, Europe or North America! Contact Electro-Com for product recommendations. >UHF technology is widely adopted in supply chain, logistics, retail, vehicle ID and asset management applications due to its relatively long read-range and low tag cost.

NFC (Near Field Communication) is a method of wireless data transfer in the HF spectrum. NFC standards include ISO/IEC 18092 and are based on the HF RFID standards ISO15693/14443. NFC offers a low-speed connection with simple setup that can be used to enable secondary wireless connections. NFC devices, including smart labels, cards and smart phones, can act as electronic identity documents and used in mobile payment, ticketing and access systems.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy or Bluetooth Smart) uses frequency hopping wireless technology in the 2.4 GHz unlicensed radio band to interconnect nearby devices. BLE, is faster, longer range and more energy efficient than its predecessors. Originally introduced in 2004, BLE adoption is now being driven by today’s fast-growing Internet of Things (IoT). For example, internet-connected devices used for personal healthcare, fitness, sports, entertainment, and location now use BLE to communicate with smartphones and tablets. Battery supported BLE tags can be attached to assets or people and communicate with BLE gateways or BLE enables smartphones.Real-time location systems (RTLS) deploy radio frequency techniques to locate people or objects in real time.
Revolutionize your sales,training and inspection workflows with webconfigurable, scalable VR/AR deployments.
We combine premium content creation with a web-based editor and portable hardware so you can deploy custom VR solutions at scale, while retaining the ability to edit and update your content in real-time.
The impact that a Virtual Reality experience creates is dependent on a variety of factors – the quality of the visuals, the narrative flow and the interaction design chief amongst them. With stunning photorealistic visuals, intuitive interaction design, premium audio production while creating immersive 3D worlds.
Augmented Reality Web Editor allows you to define new workflows, edit the virtual environment, add new 3D models and track analytics – ensuring you can update your content in a scalable, sustainable manner as your requirements change.
The launch of the Oculus Quest – a completely wireless, portable headset with enterprise grade warranty and support – completely changed that. With a simple setup process and a device management software, the Quest finally made large scale VR deployments possible.